A scatter plot is a graphical representation of data that shows the relationship between two variables. It is a popular tool used in statistics, data analysis, and scientific research to visualize and understand the relationships between different variables.
Definition
A scatter plot is a graph that displays the points or values on a set of axes. The x-axis represents one variable, while the y-axis represents another variable. Each point on the graph corresponds to a unique combination of values for the two variables being plotted.
Graph
A scatter plot typically consists of a grid with the x-axis and y-axis labels. Each data point is represented by a dot or marker on the graph, with its position determined by the values of the two variables being plotted. The points can be colored or sized differently to represent different categories or groups.
Uses
Scatter plots are used in various fields, including:
- Data analysis: To visualize and understand the relationships between different variables.
- Scientific research: To study the relationships between variables in a particular field of study.
- Business intelligence: To analyze market trends, consumer behavior, and other business-related data.
- Medical research: To study the relationships between health outcomes, risk factors, and treatment effects.
Examples
Here are some examples of scatter plots:
- Height vs. Weight: A scatter plot showing the relationship between height and weight in a population.
- Temperature vs. Humidity: A scatter plot showing the relationship between temperature and humidity in a particular region.
- Stock Prices vs. Economic Indicators: A scatter plot showing the relationship between stock prices and economic indicators, such as GDP or inflation rates.
Interpretation
To interpret a scatter plot, you need to look for patterns or relationships between the variables being plotted. Some common types of relationships include:
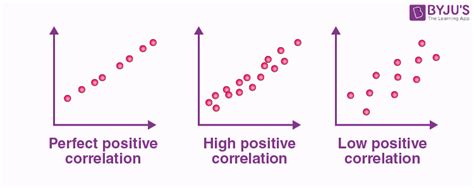
- Positive correlation: As one variable increases, the other variable also tends to increase.
- Negative correlation: As one variable increases, the other variable tends to decrease.
- No correlation: There is no apparent relationship between the two variables.
Limitations
Scatter plots have some limitations, including:
- Noise and outliers: The presence of noise or outliers in the data can affect the interpretation of the scatter plot.
- Non-linear relationships: Scatter plots may not be able to capture non-linear relationships between the variables being plotted.
- Data quality: The quality of the data used to create the scatter plot can impact its accuracy and usefulness.
****, a scatter plot is a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding the relationships between different variables. By interpreting the patterns and relationships in a scatter plot, you can gain insights into complex phenomena and make informed decisions. However, it is essential to consider the limitations of scatter plots when using them to analyze data.
References
- Wikipedia: Scatter plot (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scatter_plot)
- Khan Academy: Scatter plots (https://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat/chemical-processes/tutorials/scatter-plots/a/scatter-plots)
Note: This article is based on a combination of sources, including Wikipedia and Khan Academy.