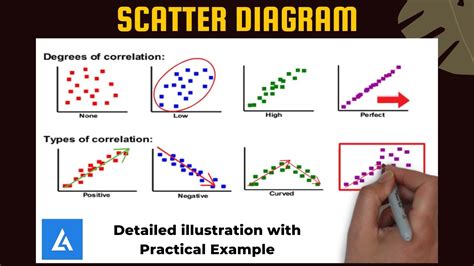
In statistics and data analysis, scattered plots are used to visualize the relationship between two variables. The points on the graph represent the relationship between the two sets of information.
Let's consider an example:
Class Average Score Scatter Plot
Suppose we collect data about exams in each of five classes from the previous year:
| Class | Period | Average Score |
|---|---|---|
| Math | 2 | 95 |
| English | 4 | 60 |
| History | 1 | 75 |
| Computer | 5 | 85 |
| Biology | 3 | 92 |
| Arts | 6 | 83 |
To create a scatter plot, we can plot the average score for each class against the period. The resulting graph shows the relationship between the two variables.
Correlation
When the two sets of given data are strongly linked to each other, we can say they have a High Correlation. There are three types of correlation:
- Positive Correlation: When both values increase or decrease together.
- Negative Correlation: When one value increases as the other decreases, and vice versa.
Solved Examples
Now, let's solve some examples based on scatter plots:
Example 1: Wheat and Food Grains
The total values of food grains (rice and wheat) imported during these years are given below. Create a scatter plot to show the relationship between wheat imports and total food grain imports.
| Year | Wheat Imports | Total Food Grain Imports |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 10,000 | 50,000 |
| 2016 | 12,000 | 60,000 |
| 2017 | 15,000 | 70,000 |
| 2018 | 18,000 | 80,000 |
| 2019 | 20,000 | 90,000 |
The scatter plot shows a positive correlation between wheat imports and total food grain imports.
Example 2: Advertising Expenses
An advertising company has recorded the following expenses and sales for three months. Create a scatter plot to show the relationship between advertising expenses and sales.
| Month | Advertising Expenses | Sales |
|---|---|---|
| January | 5,000 | 50,000 |
| February | 7,000 | 60,000 |
| March | 9,000 | 70,000 |
The scatter plot shows a positive correlation between advertising expenses and sales.
These examples demonstrate how scattered plots can be used to visualize the relationship between two variables. By analyzing the graph, we can determine the type of correlation (positive or negative) and draws about the data.
Practice Questions
If you want to practice creating scatter plots and interpreting their meaning, check out these resources:
- Corbettmaths: Scatter Graphs Practice Questions
- Mathster: Scatter Diagrams Worksheets with Answers
- 5-a-day Workbooks
Remember to use your understanding of correlation and scatter plots to solve the problems.