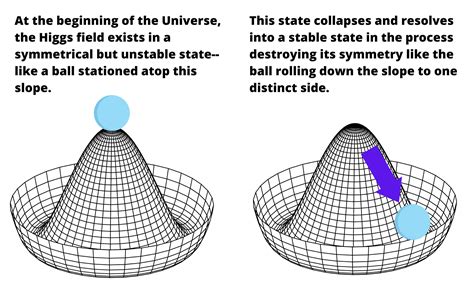
In 1964, Scottish theoretical physicist Peter Higgs proposed the existence of a new kind of field that fills the entire Universe and gives mass to all elementary particles. This field is known as the Higgs field, and it has been the subject of much debate and research in the scientific community.
The Theory Behind the Higgs Field
According to the Standard Model of quantum physics, particles acquire mass through interactions with this invisible "molasses-like" substance. The resistance an object offers to having its speed changed is known as mass, which is a fundamental property of matter. In the same way that a baseball or shotput feels resistance when thrown, particles in the Universe feel this stickiness as they move through space.
The Higgs field is thought to permeate all of space and time, and particles gain their mass by interacting with it. This interaction creates the mass we observe in the world around us. The proposal was that if you slam protons together at very high speeds, you can sometimes jiggle the molasses and sometimes flick out a little speck of the molasses, which would be a Higgs particle.
The Discovery of the Higgs Boson
In 2012, physicists from the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) announced that they had found experimental results consistent with the existence of the Higgs boson. The evidence in support of this has grown, and in 2013, Peter Higgs and Francois Englert were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for their work on the Higgs mechanism.
The detection of the Higgs boson has provided a major milestone in our understanding of the fundamental forces of nature. It has also opened up new avenues for research into the properties of the Higgs field and its role in the Universe.
Implications for Our Understanding of the Universe
The discovery of the Higgs boson may have significant implications for our understanding of the Universe. For example, it may help theoretical physicists hone in on a theory of quantum gravity that applies to our universe. It may also provide some insights into the repulsive gravity demonstrated by dark energy, which seems to permeate our observable universe.
In addition, the Higgs field may play a role in our understanding of dark matter, which is mysterious matter in our Universe that cannot be observed except through gravitational influence. The discovery of the Higgs boson has also opened up new avenues for research into the properties of mass and its role in the Universe.
The Higgs field is an elusive invisible stuff that has been the subject of much debate and research in the scientific community. The detection of the Higgs boson has provided a major milestone in our understanding of the fundamental forces of nature, and it may have significant implications for our understanding of the Universe. As we continue to study the properties of the Higgs field, we may gain a better understanding of mass and its role in the Universe, which could lead to new insights into the mysteries of quantum gravity and dark matter.
References
- Macdiarmid, P. (2012). The Discovery of the Higgs Boson. Getty Images.
- Greene, B. (2012, July 9). Brian Greene on the Higgs Field. PBS' Charlie Rose Show.
- Tufts, M. (2012, July 9). Michael Tufts on the Higgs Boson. PBS' Charlie Rose Show.