Scatter plot is a graph that is commonly used to visualize the relationship between two variables. It is often used in statistical analysis to identify patterns and trends in data. In this article, we will explore the concept of scatter plot, its types, and how it can be used to understand the relationship between variables.
What is Scatter Plot?
A scatter plot is a graph that displays the relationship between two variables by plotting individual data points on a coordinate plane. The x-axis represents one variable, while the y-axis represents the other variable. Each data point is represented by a dot or a marker on the graph.
The most common type of scatter plot is the bivariate scatter plot, which shows the relationship between two continuous variables. However, scatter plots can also be used to visualize the relationship between categorical and continuous variables, as well as between multiple variables.
Types of Scatter Plots
There are several types of scatter plots that can be used to visualize different types of relationships between variables.
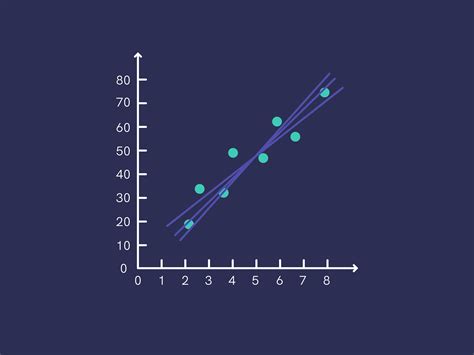
1. Linear Relationship
A linear relationship is a type of relationship where the points on the graph form a straight line. This type of relationship indicates a strong correlation between the two variables. The slope and intercept of the line can be calculated using linear regression analysis.
[Gambar 2: Linear Relationship]
2. Non-Linear Relationship
A non-linear relationship is a type of relationship where the points on the graph do not form a straight line. This type of relationship indicates that there is no strong correlation between the two variables, but there may still be some underlying pattern or trend.
[Gambar 6: Non-Linear Relationship]
3. Positive Relationship
A positive relationship is a type of relationship where as one variable increases, the other variable also increases. This type of relationship is often represented by an upward sloping line on the graph.
[Gambar 3: Positive Relationship]
4. Negative Relationship
A negative relationship is a type of relationship where as one variable increases, the other variable decreases. This type of relationship is often represented by a downward sloping line on the graph.
[Gambar 4: Negative Relationship]
5. No Relationship
A no relationship is a type of relationship where there is no underlying pattern or trend between the two variables. The points on the graph will be randomly scattered and will not form any discernible pattern.
[Gambar 5: No Relationship]
Using Scatter Plots to Identify Patterns and Trends
Scatter plots can be used to identify patterns and trends in data, as well as to visualize the relationship between variables. Some common uses of scatter plots include:
1. Identifying Outliers
A scatter plot can be used to identify outliers or data points that are significantly different from the rest of the data. This can help researchers to identify unusual patterns or trends.
[Gambar 7: Data Menyebar]
2. Visualizing the Relationship between Variables
Scatter plots can be used to visualize the relationship between two variables, such as the relationship between income and education level.
[Gambar 1: Scatter Plot]
3. Identifying Non-Linear Relationships
A scatter plot can be used to identify non-linear relationships between variables, which may indicate that there is no strong correlation between the two variables.
[Gambar 6: Non-Linear Relationship]
Limitations of Scatter Plots
While scatter plots are a powerful tool for visualizing data, they do have some limitations. Some common limitations include:
1. Limited to Bivariate Data
Scatter plots are limited to displaying bivariate data, meaning that they can only show the relationship between two variables at a time.
2. Difficult to Interpret Large Datasets
As the size of the dataset increases, it can become increasingly difficult to interpret the relationships between the variables on a scatter plot.
##, scatter plots are a powerful tool for visualizing data and identifying patterns and trends in relationships between variables. By understanding the different types of scatter plots and how they can be used to visualize relationships between variables, researchers can gain valuable insights into their data and make informed decisions about future research directions.
Rujukan:
Dahlgaard, J. J., Khanji, G. K., & Kristensen, K. (2008). Fundamentals of Total Quality Management. Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge.
Straker, D. (n.d.). Scatter diagram: How to understand it. Retrieved from http://syque.com/quality_tools/toolbook/Scatter/how.htm