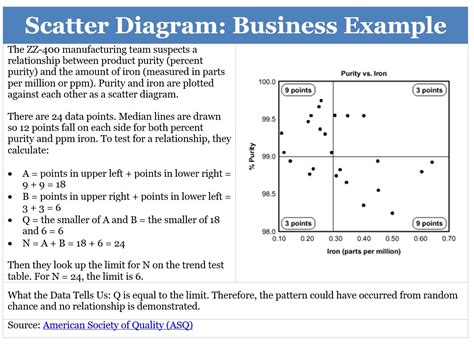
Scatter diagrams offer many benefits as an analytical tool, but also have some limitations to be aware of. In this article, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of scatter diagrams, as well as provide examples and tips on how to use them effectively.
Advantages of Scatter Diagrams
- Visualize Correlations: Scatter diagrams can help visualize correlations between data variables that may not be obvious from raw numbers alone.
- Identify Patterns, Trends, Clusters, Outliers, and Anomalies: They can identify patterns, trends, clusters, outliers, and anomalies within data sets.
- Simplify Complex Multivariate Relationships: Scatter diagrams can simplify complex multivariate relationships down to straightforward 2D plots.
- Intuitive Charts: They are intuitive charts that are easy for broad audiences to interpret.
- Assess Cause-and-Effect Relationships: They help assess cause-and-effect relationships between inputs and outputs.
- Low-Resource Charts: Scatter diagrams are low-resource charts that are fast and easy to create.
- Provide Useful Evidence: They provide useful evidence to support theories, hypotheses, and arguments with quantitative backing.
- Aid Forecasting and Prediction: They aid forecasting, prediction, and data-driven decision-making.
Disadvantages of Scatter Diagrams
- Only Display Correlation: They only display correlation, not causation between variables.
- Prone to Biases: They are prone to biases based on limited data points in smaller data sets.
- Difficulty in Plotting Multiple Variables: It is difficult to plot more than two or three variables effectively.
- Cannot Convey Detailed Numerical Analysis: Scatter diagrams cannot convey detailed numerical analysis and statistics.
- Challenging to Display Large Data Sets: It is challenging to display large data sets without overcrowding.
- Audience May Draw Incorrects: The audience may draw incorrects from scatter diagrams without statistical expertise.
Example of Scatter Diagram
The scatter diagram can be utilized in a variety of industries and applications to compare two variables for any data model. For example, as a quality manager, you use a scatter diagram to analyze the relationship between machine runtime hours and defect rate in your manufacturing process. By plotting this data into a scatter diagram, you see that there is a positive correlation between high machine runtime and more frequent defects.
Tips for PMP Exam
For your PMP certification exam, you must understand what scatter diagrams are, their types, and how they are used for project quality management. These diagrams help in identifying and analyzing the relationships between two variables in a project and are used for data representation in the Manage Quality and Control Quality PMBOK guide processes.
****, scatter diagrams are simple yet powerful quality tools for visualizing connections and patterns in data. By plotting two variables on the X and Y axes, you can identify correlations, clusters, trends, and outliers. Scatter diagrams help assess relationships between inputs and outputs to find factors that influence quality and performance. While they show correlation and not causation, scatter plots enable smarter data-driven decisions through understandable 2D visuals.
FAQs
- What is a Scatter Diagram in the Context of Project Quality Management?
A scatter diagram in project quality management is a graphical tool used to understand the relationship between two variables. - Why is a Scatter Diagram Important in TQM?
A scatter diagram is crucial in Total Quality Management (TQM) as it helps visualize correlations between two variables, assisting in identifying dependencies, predicting outcomes, pinpointing issues, and guiding improvements. - What is the Difference Between Correlation and Scatter Diagram?
Correlation is a statistical measure expressing the degree of relationship between two variables, ranging from -1 (negative correlation) to +1 (positive correlation). A scatter diagram is a graphical representation used to visually depict this relationship or lack thereof between two variables.